Welcome to DART protocol demonstration !

Disclaimer on the Use of the Name "DART"
Protocol Name: DART (Domain Aware Routing Technology)
Author: lishi.china@qq.com
Date of Release: September, 2025
The DART protocol is a network communication protocol designed by an independent developer and released freely to the public. It aims to explore an alternative solution to the shortage of IPv4 addresses, addressing the difficulties in promoting IPv6 due to its incompatibility with IPv4.
We hereby declare:
The term “DART” used in this protocol stands solely for “Domain Aware Routing Technology,” and is intended to describe the key technical feature of the protocol. It bears no relation to, nor any affiliation with, the Dart programming language developed by Google.
Any mention of the "DART" protocol refers exclusively to this network communication protocol, and not to any programming language or other similarly named products.
Welcome!
If you are opening this website for the first time, the topology/path of your visit to this website is likely to be as follows:
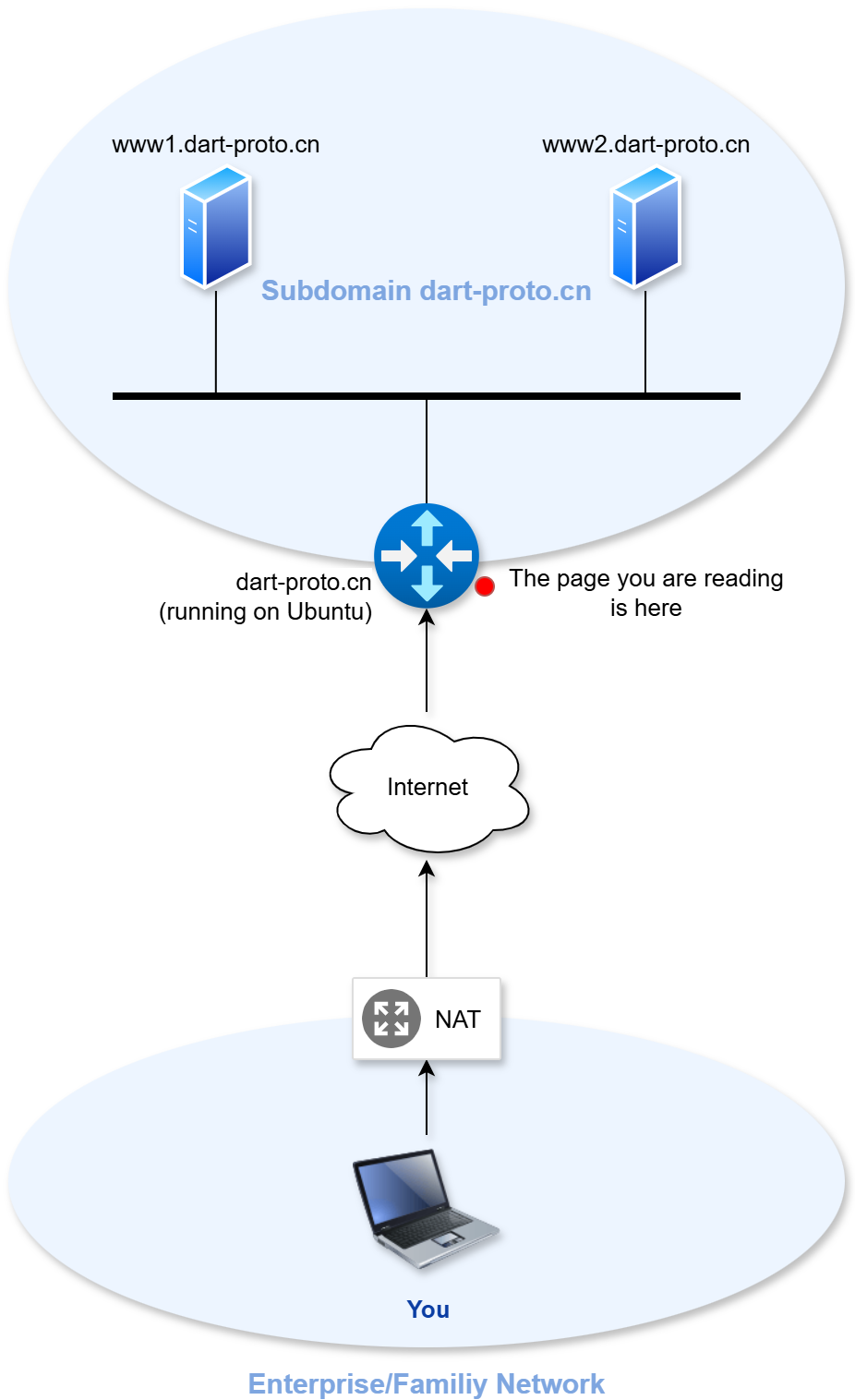
The red dots in the image indicate the location of the webpage you are currently viewing (it is not important if there are 0, 1, or multiple NAT gateways between you and the Internet).
The purpose of this website is to demonstrate how to expand more address space with the support of DART protocol.
- With the support of the DART protocol, each domain (such as the dart-proto.cn domain you are currently visiting) can accommodate a number of hosts equivalent to the entire IPv4 address space (there are 2³² addresses in the IPv4 address space, with nearly 4.3 billion hosts).
- Moreover, if the dart proto.cn domain is further derived into subdomains, each subdomain can also accommodate 2³² hosts.
- The maximum length of a domain name in the DNS system is 256 bytes, and the number of subdomains that can be derived from a domain name can actually be considered infinite. Therefore, the number of hosts that can be accommodated in the DART protocol is also infinite.
In the dart-proto.cn domain as a demonstration, there are 3 hosts:
- dart-proto.cn (with the role of gateway, therefore the router icon is used in the topology diagram),
- www1.dart-proto.cn
- www2.dart-proto.cn
All of which have enabled web services. Meanwhile, all 3 domain names are resolved to the same IP address (124.71.175.125) in the DNS system. That is to say, if you access these 3 domains through a browser at this time, you will see the same website (i.e. the current website).
Access servers inside the domain
How can I access the web services provided on the servers inside the domain? You need to make your host support DART protocol.
You have 2 ways to make your host support DART protocol:
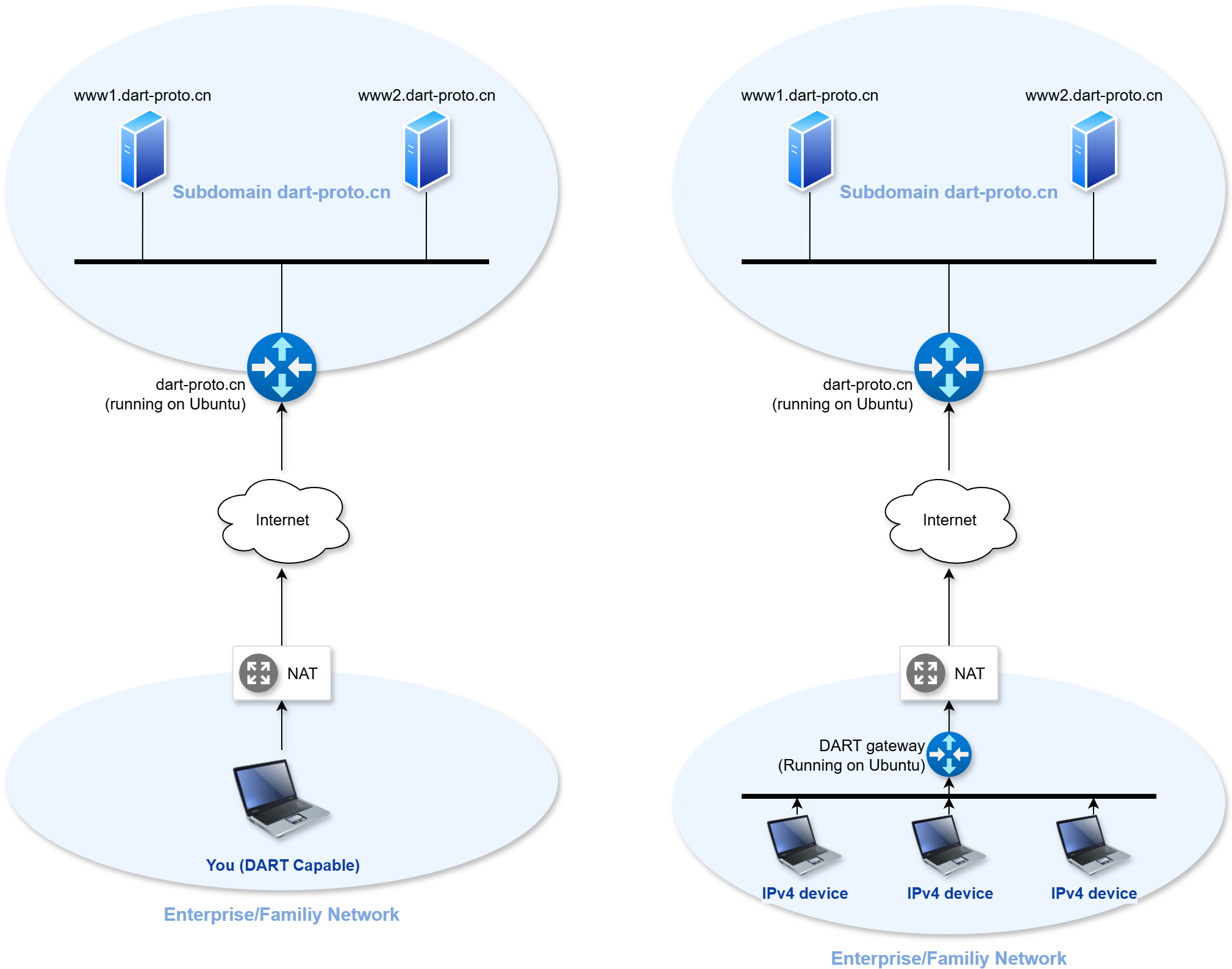
Method 1: Install a service program on your computer
At present, installation packages are provided for 64 bit Windows systems, supporting Windows 10/11 (other 64 bit versions of Windows should theoretically support it, but have not been tested).
Installation package & Source(github):
https://github.com/rancho-dart/DartWinDivert/releases/latest
- The DART protocol is inherently dual-stack, and installing DartWinDivert will not affect the host's access to IPv4 hosts
- After installing DartWinDivert, if clicking on www1.dart-proto.cn and www2.dart-proto.cn still opens dart-proto.cn, please run the following command to clear the DNS cache:
ifconfig /flushdns
Method 2: Deploy a DART enabled gateway at the exit of your LAN
- After deploying the DART gateway, all internal hosts can access external DART hosts without any special configuration.
- In the dart-proto.cn domain, only the host dart-proto.cn has the dart_forwarder gateway software installed.
- Both www1.dart-proto.cn and www2.dart-proto.cn are native Ubuntu systems with nginx services.
- If the domain name is registered in DNS and delegated to the DART gateway, the internal network host can also be accessed by external DART hosts, and the internal network host does not require any special configration
- that is to say, if there are IPv4 devices on your intranet that cannot upgrade the protocol stack but still wish to access them from the Internet, DART protocol can meet your wishes.
The source code is written in Go language and has been debugged on Ubuntu 24 system.
Source:rancho-dart/dart_forwarder
If the intranet is configured with a private network segment, the DART gateway will automatically enable NAT44, allowing intranet hosts to simultaneously access DART-Ready devices and IPv4-Only hosts.
After the DART gateway starts:
- If the client obtains its address via DHCP, please re-trigger DHCP to ensure the client receives an IP from the DART gateway.
- If the client is using a static address, please make sure the client information is configured on the downstream interface of the DART gateway.
Introduction about dart_forwarder
As a service running on the Ubuntu system, dart_forwarder includes the following contents:
- DHCP Server
- DNS Server
- DART forwarder
- NAT-DART-4
- NAT44
The Ubuntu operating system comes with a local DNS service installed by default. Installing dart_forwarder requires shutting down the default DNS service. The README file in the source code will guide you through the entire process of compilation, installation, and configuration.
NAT44 is not a part of the DART protocol, but it does not conflict with DART either. The DART protocol allows internal networks to use the entire IPv4 address space for addressing. However, if the service sees a private network address used in the internal network during startup, it will automatically start NAT44 to support accessing hosts on the Internet that do not support the DART protocol. This feature is very valuable for smooth upgrades.
Details
We provide a detailed introduction to the design, operation mode, and upgrade route of the DART protocol on two servers inside the domain.